General Insurance Australia
The industry is forecast to improve over the next five years, as local and global economies are projected to record stronger growth. Interest rates are expected to rise too, which will likely boost investment income for insurers. The industry includes general insurers and reinsurers. General insurers underwrite insurance policies to cover individuals and businesses' financial loss associated with property, casualty, liability and other risks. Underwriting involves assuming risks and assigning premiums. ]
Industry Report
General Insurance in Australia
The industry is forecast to improve over the next five years, as local and global economies are projected to record stronger growth. Interest rates are expected to rise too, which will likely boost investment income for insurers.
The industry includes general insurers and reinsurers. General insurers underwrite insurance policies to cover individuals and businesses' financial loss associated with property, casualty, liability and other risks. Underwriting involves assuming risks and assigning premiums. Reinsurers assume all or part of the risk associated with existing insurance policies underwritten by other insurers.
The occurrence of natural disasters has resulted in a rise in the number of claims, forcing industry operators to raise premiums. The COVID-19 pandemic has also led to a shift in types of insurance claims.
DEMAND DETERMINANTS
OVERALL ECONOMIC ACTIVITY | CONSUMER WEALTH | DEMOGRAPHICS | BUSINESS AND CONSUMER CONFIDENCE | RISK PROFILES | PREMIUMS
Demand for products from the General Insurance industry is affected by many factors including: overall economic activity, consumer wealth, demographics, business and consumer confidence, risk profiles and premiums. Wider economic activity affects insurance demand through exposure to risk. Higher employment leads to more risk associated with workers' compensation. A strong economy and labour market increases disposable income, driving household consumption and wealth and therefore, generates greater demand for insurance. Similarly, any decrease in overall economic activity can reduce household coverage, as wealth and consumer expenditure decline. Demographics also influence insurance demand, with individuals' coverage and expenditure increasing as they age. Premiums affect coverage levels and the volume of policies offered. Premium increases can constrain demand and reduce coverage as consumers self-insure when insurance costs outweigh potential payout gains.
OUTLOOK 2021 - 2026
Industry revenue is projected to grow over the next 5 years; driven by the anticipated economic recovery from the recession which is likely to generate demand for general insurance products, providing insurers with the opportunity to grow premium revenue. Additionally, forecasted growth in the cash rate and bond yields will enable operators to generate higher investment returns. Adversely, strong industry competition is forecast to put pressure on profit margins as well as the effects of the 2019 Royal Commission into Misconduct in the Banking, Superannuation and Financial Services which is to come into effect as at 1 July 2021.
The major players are projected to continue to dominate the industry, intensifying price competition and increasing policy coverage. Strong competition is likely to impact Small/Medium Enterprises the most. Large insurers hold more capital, so they can bear higher pricing risks and are better placed to add further coverage to existing policies. Online aggregators have driven a rise in competition, as greater price transparency has generated additional pressure on firms to compete on price.
Larger insurers have a history of aggressive expansion through M&A, and further activity is projected which is expected to reduced industry enterprise and establishment numbers. Employment numbers are also anticipated to drop marginally, as key players continue to acquire smaller operators.
External competition is likely to increase as non-traditional insurers and large technology companies, such as Google, Facebook and Amazon, are anticipated to push into the industry. These companies have been making inroads into online user experience and customisation, and have demonstrated an ability to quickly enter and disrupt new markets. However, the pandemic has forced insurers to accelerate the adoption of digital technology.
The industry will likely face some technological disruption. While technological developments could increase competition within the industry, it also creates opportunities for industry players to to expand, given the growing popularity of cloud computing and business being conducted online.
Cyber insurance is becoming an increasingly popular area of general insurance, which typically covers losses from data theft and other IT-related risks. This market remains largely untapped and presents an opportunity for operators, given the complexity and risks of the cyber landscape.
Source: IBISWorld | General Insurance in Australia, March 2021
LOOKING TO CREATE VALUE IN YOUR ORGANISATION? LET US HELP.
Whiteark is not your average consulting firm, we have first-hand experience in delivering transformation programs for private equity and other organisations with a focus on people just as much as financial outcomes. We understand that execution is the hardest part, and so we roll our sleeves up and work with you to ensure we can deliver the required outcomes for the business.
Our co-founders have a combined experience of over 50 years’ working as Executives in organisations delivering outcomes for shareholders. Reach out for a no obligation conversation on how we can help you. Contact us on whiteark@whiteark.com.au
A Comprehensive Covid Report
This in-depth 28+ page report takes a deep dive into 18 different industries, looking at how they have been impacted differently by the Covid-19 global pandemic, and what industries can do as we enter the recovery and regeneration phase. Source: IbisWorld. Note: This is based on Stage 4 Restrictions.
A closer look at how industries have been affected by the pandemic that swept the world.
Source: IbisWorld. Note: This is based on Stage 4 Restrictions.
Recently, we asked our followers what they wanted. What would be truly helpful to them in these unprecedented times, and the answer? Industry specific breakdowns.
We all know that every sector has been affected in one way or another, there's heaps of generalised statements floating around that provide helpful overviews. But what people were after was a more specific breakdown of exactly what the impact would be to their area of operations and ideas around how they could pivot, adapt and thrive as we move forward into the new world normal.
So, here it is. A comprehensive deep dive into 18 different industries - we hope you enjoy the read.
What's in the report?
Setting the Scene
Impact: How exposed is your industry?
Impact Analysis: Exposure Definitions
Industry Deep Dives
Accommodation & Food Services
Arts & Recreation Services
Education & Training
Manufacturing
Professional, Scientific & Technical Services
Retail Trade
Mining
Construction
Health Care & Social Assistance
Transport Postal & Warehousing
Administrative & Support Services
Public Administration & Safety
Agriculture, Forestry & Fishing
Wholesale Trade
Electricity, Gas, Water & Waste Services
Finance
Information Media & Telecommunications
Rental, Hiring & Real Estate Services
Bonus Article: The Importance Of Innovation
Global Trends to emerge post Covid-19
We take a closer look at the changes affecting countries across the world as we emerge from the changes caused by Covid-19. Source: Frost & Sullivan 9 Critical Trends Reshaping all Industries Post-COVID, 2020
We take a closer look at the trends affecting countries across the world as we emerge form the changes caused by Covid-19.
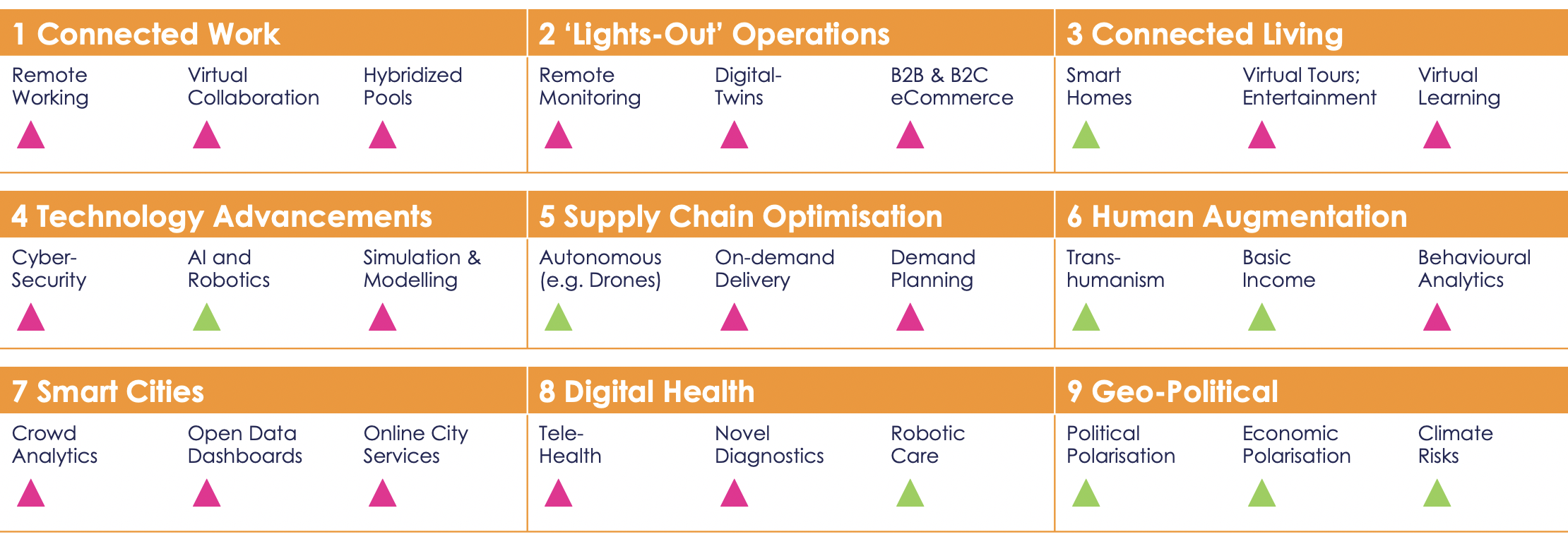
1. Connected Work
Connected work scenarios will drive the need for cloud everything. New subscription-based models will see growth in demand for unified communications as a service offerings.
2. ‘Lights-Out’ Operations
Autonomous “lights out” operations will drive demand for remote asset management solutions, and service providers will focus on data management strategies and data-driven business models.
3. Connected Living
An increased adoption of contactless surfaces post-pandemic will drive home automation and security markets.
4. Technology Advancements
Pandemic preparedness will speed up AI deployment and accelerate the pace of AI innovation.
5. Supply Chain Optimisation
Seamless integration of end-to-end digital supply chains will increase traceability, sustainability, and transparency within the supply chain ecosystem.
6. Human Augmentation
The adoption rate of customer behaviour analytics by enterprises will grow by 20% for the period 2019-2025.
7. Smart Cities
Increased spending on technology by smart cities will lead to a surge in the adoption of digital tools like crowd analytics, and increased focus on developing digital platforms and apps for citizens.
8. Digital Health
Digital health driven by telemedicine and robotic care will become the new standard of care delivery. Will require an increase in the number of service and technology providers.
9. Geo-Political
To protect themselves from economic fallout due to COVID, global organisations are coming together to restore geo-political and economic balance.
Looking to capitalise on these trends and ensure your business is poised for success? Let us help.
Whiteark is not your average consulting firm, we have first-hand experience in delivering transformation programs for private equity and other organisations with a focus on people just as much as financial outcomes. We understand that execution is the hardest part, and so we roll our sleeves up and work with you to ensure we can deliver the required outcomes for the business. Our co-founders have a combined experience of over 50 years’ working as Executives in organisations delivering outcomes for shareholders. Reach out for a no obligation conversation on how we can help you. Contact us on whiteark@whiteark.com.au
SOURCE: Frost & Sullivan 9 Critical Trends Reshaping all Industries Post-COVID, 2020
Household Consumption
We take a closer look at the impact of Covid-19 on household consumption and spending. Data shows that the household saving ratio hit heights not seen since the early 1970s. Reasons include: Precautionary, Investment or retirement, First home, Reduce loans.
Covid Impact Report
Household Consumption
Covid-19 has caused household saving ratios to hit heights not seen since the early 1970s.
OVERVIEW
Household Consumption Spending:
50% of households expect to have less income available after meeting commitments.
Disposable income expectations in a year from now:
Increase: 17%
Decrease: 50%
Remain the Same: 25%
Unsure: 8%
Household disposable income outlook…
Employment is increasing as pandemic restrictions ease
Population growth has slowed from 1.5% to 0.5% - less people receiving income than previously expected
Wages growth has slowed from a low 2.2% to 1.8% and may decline further given the weak labour market
Federal income support will be progressively reduced over the next six months
Interest payments on savings have declined and so have share market dividends
Household Consumption Expenditure Outlook
Household consumption expenditure growth will improve slowly as more spending options
become available
Weak income growth will constrain the rate of growth, although a build up of savings is likely
to reduce slowly and support spending to some degree
In annual growth terms, spending will likely still be in decline over the September, December,
and March 2021 quarters
Underlying growth will then settle at around 3.5% to 4%, which is similar to the growth rate
before the pandemic
Pessimistic estimate of underlying growth in consumer spending is 1.5% to 2% and optimistic
estimate is 5% to 6%. The optimistic estimate is still below the pre-GFC growth rate of 5% to 9%
*Data Source: Foreseechange, Charlie Nelson
Consumer patterns and implications for brands & retail
Covid-19 has created several consumer segments as a result of varying attitudes. Concerns are centred around health, the economy (including income and unemployment), and climate change which is still a prominent issue. 80% are not willing to return to life as it was, driven by ongoing concerns about health and finances but also as a result of rethinking and resetting priorities.
Covid Impact Report
Consumer Patterns & Implications for Brand & Retail
Covid-19 has created several new consumer segments as a result of varying attitudes and spending habits are changing.
OVERVIEW
Consumer concerns are centred around health, the economy (including income and unemployment), and climate change which is still a prominent issue.
80% are not willing to return to life as it was.
Driven by ongoing concerns about health and finances but also as a result of rethinking and resetting priorities.
50% expect to have less disposable income.
Driven by high unemployment and the imminent reduction of government income assistance.
A high priority to build savings.
As a precaution, to buy residential property to live in, or to invest.
Only 9% feel they have discretionary funds and want to spend on discretionary items.
Consumers have adapted their shopping behaviour.
As a result of the pandemic and lockdown restrictions; consumers have adapted to online channels at the speed of lightning.
With more consumers adopting new ways of doing things, the online grocery channel has increased market share.
Convenience customers are going to drive a surge in e-commerce
Retail entrepreneur Ruslan Kogan, says the next wave of e-commerce growth in Australia will be driven by consumers interested in convenience as much as price.
Kogan predicts e-commerce will surge from 8% to 30%.
If Kogan’s prediction is accurate, that still leaves 70% for physical shops (which may also sell online)for shoppers who prefer local, personal customer service, unique merchandise, instant gratification, or other attributes satisfied best by physical shopping.
Keeping it local…
Independent and specialty stores are benefiting from consumers shopping closer to their location and wanting to support local businesses.
Key reasons consumers are shopping locally:
I’m supporting local businesses
I’m shopping more at stores that are closer to my location
I was looking for better quality products
I was looking for products that I couldn’t find at larger retailers
I was looking for better prices
I always shop at this store
Shopping locally is more important for Insulated spenders.
Constrained or insulated?
As published in Nielsen’s “Reboot or Rebound – The New Normal For Australia” communication, the polarisation of consumer spending habits continues…
Insulated spenders prioritise convenience whilst Constrained spenders prioritise value. Constrained households do not necessarily correlate to lower income.
In this report we unpack how brands and retail can cater for the two types of spenders: constrained and insulated and what trends we can expect to see as the retail landscape continues to evolve and change.
*Data Source: Foreseechange, Charlie Nelson